SQL Manual
SQL Manual
DATABASE MANAGEMENT
For more details, see document Operate-Metadata.
Create Database
IoTDB > create database root.ln
IoTDB > create database root.sgcc
IoTDB> CREATE DATABASE root.ln.wf01
Msg: 300: root.ln has already been created as database.
IoTDB> create database root.ln.wf01
Msg: 300: root.ln has already been created as database.Show Databases
IoTDB> SHOW DATABASES
IoTDB> SHOW DATABASES root.**Delete Database
IoTDB > DELETE DATABASE root.ln
IoTDB > DELETE DATABASE root.sgcc
// delete all data, all timeseries and all databases
IoTDB > DELETE DATABASE root.**Count Databases
IoTDB> count databases
IoTDB> count databases root.*
IoTDB> count databases root.sgcc.*
IoTDB> count databases root.sgccSetting up heterogeneous databases (Advanced operations)
Set heterogeneous parameters when creating a Database
CREATE DATABASE root.db WITH SCHEMA_REPLICATION_FACTOR=1, DATA_REPLICATION_FACTOR=3, SCHEMA_REGION_GROUP_NUM=1, DATA_REGION_GROUP_NUM=2;Adjust heterogeneous parameters at run time
ALTER DATABASE root.db WITH SCHEMA_REGION_GROUP_NUM=1, DATA_REGION_GROUP_NUM=2;Show heterogeneous databases
SHOW DATABASES DETAILSTTL
Set TTL
IoTDB> set ttl to root.ln 3600000
IoTDB> set ttl to root.sgcc.** 3600000
IoTDB> set ttl to root.** 3600000Unset TTL
IoTDB> unset ttl to root.ln
IoTDB> unset ttl to root.sgcc.**
IoTDB> unset ttl to root.**Show TTL
IoTDB> SHOW ALL TTL
IoTDB> SHOW TTL ON StorageGroupNamesSCHEMA TEMPLATE
For more details, see document Operate-Metadata.
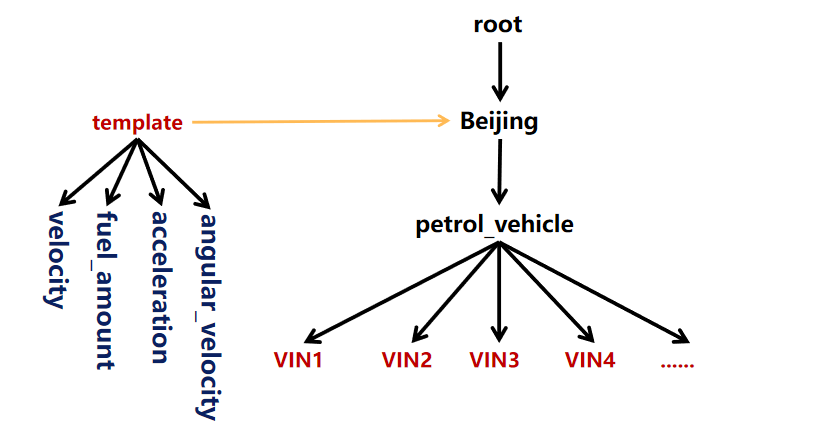
Create template(s1 int, s2 float) on root.sg
Create device root.sg.d1
Create Schema Template
Example 1: Create a template containing two non-aligned timeseires
IoTDB> create schema template t1 (temperature FLOAT encoding=RLE, status BOOLEAN encoding=PLAIN compression=SNAPPY)Example 2: Create a template containing a group of aligned timeseires
IoTDB> create schema template t2 aligned (lat FLOAT encoding=Gorilla, lon FLOAT encoding=Gorilla)The lat and lon measurements are aligned.
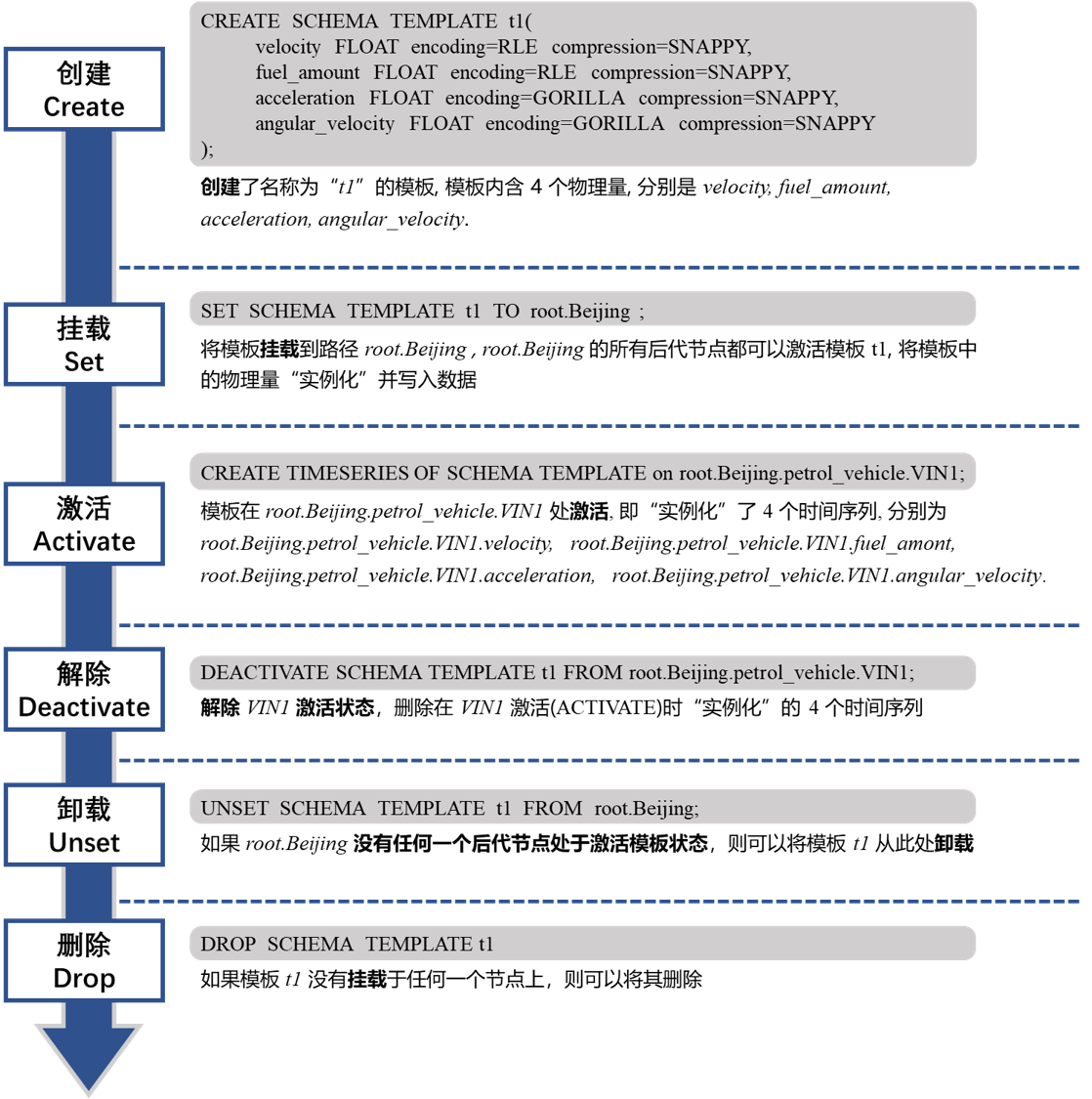
Set Schema Template
IoTDB> set schema template t1 to root.sg1.d1Activate Schema Template
IoTDB> set schema template t1 to root.sg1.d1
IoTDB> set schema template t2 to root.sg1.d2
IoTDB> create timeseries using schema template on root.sg1.d1
IoTDB> create timeseries using schema template on root.sg1.d2Show Schema Template
IoTDB> show schema templates
IoTDB> show nodes in schema template t1
IoTDB> show paths set schema template t1
IoTDB> show paths using schema template t1Deactivate Schema Template
IoTDB> delete timeseries of schema template t1 from root.sg1.d1
IoTDB> deactivate schema template t1 from root.sg1.d1
IoTDB> delete timeseries of schema template t1 from root.sg1.*, root.sg2.*
IoTDB> deactivate schema template t1 from root.sg1.*, root.sg2.*Unset Schema Template
IoTDB> unset schema template t1 from root.sg1.d1Drop Schema Template
IoTDB> drop schema template t1Alter Schema Template
IoTDB> alter schema template t1 add (speed FLOAT encoding=RLE, FLOAT TEXT encoding=PLAIN compression=SNAPPY)TIMESERIES MANAGEMENT
For more details, see document Operate-Metadata.
Create Timeseries
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature with datatype=FLOAT,encoding=RLE
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.hardware with datatype=TEXT,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.sgcc.wf03.wt01.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.sgcc.wf03.wt01.temperature with datatype=FLOAT,encoding=RLE- From v0.13, you can use a simplified version of the SQL statements to create timeseries:
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature with datatype=FLOAT,encoding=RLE
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.hardware with datatype=TEXT,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.sgcc.wf03.wt01.status with datatype=BOOLEAN,encoding=PLAIN
IoTDB > create timeseries root.sgcc.wf03.wt01.temperature with datatype=FLOAT,encoding=RLE- Notice that when in the CREATE TIMESERIES statement the encoding method conflicts with the data type, the system gives the corresponding error prompt as shown below:
IoTDB > create timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.status WITH DATATYPE=BOOLEAN, ENCODING=TS_2DIFF
error: encoding TS_2DIFF does not support BOOLEANCreate Aligned Timeseries
IoTDB> CREATE ALIGNED TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.GPS(latitude FLOAT encoding=PLAIN compressor=SNAPPY, longitude FLOAT encoding=PLAIN compressor=SNAPPY)Delete Timeseries
IoTDB> delete timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.status
IoTDB> delete timeseries root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature, root.ln.wf02.wt02.hardware
IoTDB> delete timeseries root.ln.wf02.*
IoTDB> drop timeseries root.ln.wf02.*Show Timeseries
IoTDB> show timeseries root.**
IoTDB> show timeseries root.ln.**
IoTDB> show timeseries root.ln.** limit 10 offset 10
IoTDB> show timeseries root.ln.** where timeseries contains 'wf01.wt'
IoTDB> show timeseries root.ln.** where dataType=FLOATCount Timeseries
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.**
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.**
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.*.*.status
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.wt01.status
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** WHERE TIMESERIES contains 'sgcc'
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** WHERE DATATYPE = INT64
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** WHERE TAGS(unit) contains 'c'
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** WHERE TAGS(unit) = 'c'
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** WHERE TIMESERIES contains 'sgcc' group by level = 1
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.** GROUP BY LEVEL=1
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.** GROUP BY LEVEL=2
IoTDB > COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.* GROUP BY LEVEL=2Tag and Attribute Management
create timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1(temprature) with datatype=FLOAT, encoding=RLE, compression=SNAPPY tags(tag1=v1, tag2=v2) attributes(attr1=v1, attr2=v2)- Rename the tag/attribute key
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 RENAME tag1 TO newTag1- Reset the tag/attribute value
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 SET newTag1=newV1, attr1=newV1- Delete the existing tag/attribute
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 DROP tag1, tag2- Add new tags
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 ADD TAGS tag3=v3, tag4=v4- Add new attributes
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 ADD ATTRIBUTES attr3=v3, attr4=v4- Upsert alias, tags and attributes
add alias or a new key-value if the alias or key doesn't exist, otherwise, update the old one with new value.
ALTER timeseries root.turbine.d1.s1 UPSERT ALIAS=newAlias TAGS(tag3=v3, tag4=v4) ATTRIBUTES(attr3=v3, attr4=v4)- Show timeseries using tags. Use TAGS(tagKey) to identify the tags used as filter key
SHOW TIMESERIES (<`PathPattern`>)? timeseriesWhereClausereturns all the timeseries information that satisfy the where condition and match the pathPattern. SQL statements are as follows:
ALTER timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.hardware ADD TAGS unit=c
ALTER timeseries root.ln.wf02.wt02.status ADD TAGS description=test1
show timeseries root.ln.** where TAGS(unit)='c'
show timeseries root.ln.** where TAGS(description) contains 'test1'- count timeseries using tags
COUNT TIMESERIES (<`PathPattern`>)? timeseriesWhereClause
COUNT TIMESERIES (<`PathPattern`>)? timeseriesWhereClause GROUP BY LEVEL=<INTEGER>returns all the number of timeseries that satisfy the where condition and match the pathPattern. SQL statements are as follows:
count timeseries
count timeseries root.** where TAGS(unit)='c'
count timeseries root.** where TAGS(unit)='c' group by level = 2create aligned timeseries
create aligned timeseries root.sg1.d1(s1 INT32 tags(tag1=v1, tag2=v2) attributes(attr1=v1, attr2=v2), s2 DOUBLE tags(tag3=v3, tag4=v4) attributes(attr3=v3, attr4=v4))The execution result is as follows:
IoTDB> show timeseries
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+
| timeseries|alias| database|dataType|encoding|compression| tags| attributes|deadband|deadband parameters|
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+
|root.sg1.d1.s1| null| root.sg1| INT32| RLE| SNAPPY|{"tag1":"v1","tag2":"v2"}|{"attr2":"v2","attr1":"v1"}| null| null|
|root.sg1.d1.s2| null| root.sg1| DOUBLE| GORILLA| SNAPPY|{"tag4":"v4","tag3":"v3"}|{"attr4":"v4","attr3":"v3"}| null| null|
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+Support query:
IoTDB> show timeseries where TAGS(tag1)='v1'
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+
| timeseries|alias| database|dataType|encoding|compression| tags| attributes|deadband|deadband parameters|
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+
|root.sg1.d1.s1| null| root.sg1| INT32| RLE| SNAPPY|{"tag1":"v1","tag2":"v2"}|{"attr2":"v2","attr1":"v1"}| null| null|
+--------------+-----+-------------+--------+--------+-----------+-------------------------+---------------------------+--------+-------------------+The above operations are supported for timeseries tag, attribute updates, etc.
NODE MANAGEMENT
For more details, see document Operate-Metadata.
Show Child Paths
SHOW CHILD PATHS pathPatternShow Child Nodes
SHOW CHILD NODES pathPatternCount Nodes
IoTDB > COUNT NODES root.** LEVEL=2
IoTDB > COUNT NODES root.ln.** LEVEL=2
IoTDB > COUNT NODES root.ln.wf01.** LEVEL=3
IoTDB > COUNT NODES root.**.temperature LEVEL=3Show Devices
IoTDB> show devices
IoTDB> show devices root.ln.**
IoTDB> show devices root.ln.** where device contains 't'
IoTDB> show devices with database
IoTDB> show devices root.ln.** with databaseCount Devices
IoTDB> show devices
IoTDB> count devices
IoTDB> count devices root.ln.**INSERT & LOAD DATA
Insert Data
For more details, see document Write-Delete-Data.
Use of INSERT Statements
- Insert Single Timeseries
IoTDB > insert into root.ln.wf02.wt02(timestamp,status) values(1,true)
IoTDB > insert into root.ln.wf02.wt02(timestamp,hardware) values(1, 'v1')- Insert Multiple Timeseries
IoTDB > insert into root.ln.wf02.wt02(timestamp, status, hardware) VALUES (2, false, 'v2')
IoTDB > insert into root.ln.wf02.wt02(timestamp, status, hardware) VALUES (3, false, 'v3'),(4, true, 'v4')- Use the Current System Timestamp as the Timestamp of the Data Point
IoTDB > insert into root.ln.wf02.wt02(status, hardware) values (false, 'v2')Insert Data Into Aligned Timeseries
IoTDB > create aligned timeseries root.sg1.d1(s1 INT32, s2 DOUBLE)
IoTDB > insert into root.sg1.d1(time, s1, s2) aligned values(1, 1, 1)
IoTDB > insert into root.sg1.d1(time, s1, s2) aligned values(2, 2, 2), (3, 3, 3)
IoTDB > select * from root.sg1.d1Load External TsFile Tool
For more details, see document Import-Export-Tool.
Load with SQL
- Load a single tsfile by specifying a file path (absolute path).
load '/Users/Desktop/data/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile'load '/Users/Desktop/data/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile' sglevel=1load '/Users/Desktop/data/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile' onSuccess=deleteload '/Users/Desktop/data/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile' sglevel=1 onSuccess=delete
- Load a batch of files by specifying a folder path (absolute path).
load '/Users/Desktop/data'load '/Users/Desktop/data' sglevel=1load '/Users/Desktop/data' onSuccess=deleteload '/Users/Desktop/data' sglevel=1 onSuccess=delete
Load with Script
./load-rewrite.bat -f D:\IoTDB\data -h 192.168.0.101 -p 6667 -u root -pw rootDELETE DATA
For more details, see document Write-Delete-Data.
Delete Single Timeseries
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time<=2017-11-01T16:26:00;
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time>=2017-01-01T00:00:00 and time<=2017-11-01T16:26:00;
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time < 10
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time <= 10
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time < 20 and time > 10
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time <= 20 and time >= 10
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time > 20
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time >= 20
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time = 20
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.status where time > 4 or time < 0
Msg: 303: Check metadata error: For delete statement, where clause can only contain atomic
expressions like : time > XXX, time <= XXX, or two atomic expressions connected by 'AND'
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.statusDelete Multiple Timeseries
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02 where time <= 2017-11-01T16:26:00;
IoTDB > delete from root.ln.wf02.wt02.* where time <= 2017-11-01T16:26:00;
IoTDB> delete from root.ln.wf03.wt02.status where time < now()
Msg: The statement is executed successfully.Delete Time Partition (experimental)
IoTDB > DELETE PARTITION root.ln 0,1,2QUERY DATA
For more details, see document Query-Data.
SELECT [LAST] selectExpr [, selectExpr] ...
[INTO intoItem [, intoItem] ...]
FROM prefixPath [, prefixPath] ...
[WHERE whereCondition]
[GROUP BY {
([startTime, endTime), interval [, slidingStep]) |
LEVEL = levelNum [, levelNum] ... |
TAGS(tagKey [, tagKey] ... ) |
VARIATION(expression[,delta][,ignoreNull=true/false]) |
CONDITION(expression,[keep>/>=/=/</<=]threshold[,ignoreNull=true/false]) |
SESSION(timeInterval) |
COUNT(expression, size[,ignoreNull=true/false])
}]
[HAVING havingCondition]
[ORDER BY sortKey {ASC | DESC}]
[FILL ({PREVIOUS | LINEAR | constant})]
[SLIMIT seriesLimit] [SOFFSET seriesOffset]
[LIMIT rowLimit] [OFFSET rowOffset]
[ALIGN BY {TIME | DEVICE}]Basic Examples
Select a Column of Data Based on a Time Interval
IoTDB > select temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time < 2017-11-01T00:08:00.000Select Multiple Columns of Data Based on a Time Interval
IoTDB > select status, temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000;Select Multiple Columns of Data for the Same Device According to Multiple Time Intervals
IoTDB > select status,temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where (time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000) or (time >= 2017-11-01T16:35:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000);Choose Multiple Columns of Data for Different Devices According to Multiple Time Intervals
IoTDB > select wf01.wt01.status,wf02.wt02.hardware from root.ln where (time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000) or (time >= 2017-11-01T16:35:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000);Order By Time Query
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time > 1 order by time desc limit 10;SELECT CLAUSE
Use Alias
IoTDB > select s1 as temperature, s2 as speed from root.ln.wf01.wt01;Nested Expressions
Nested Expressions with Time Series Query
IoTDB > select a,
b,
((a + 1) * 2 - 1) % 2 + 1.5,
sin(a + sin(a + sin(b))),
-(a + b) * (sin(a + b) * sin(a + b) + cos(a + b) * cos(a + b)) + 1
from root.sg1;
IoTDB > select (a + b) * 2 + sin(a) from root.sg
IoTDB > select (a + *) / 2 from root.sg1
IoTDB > select (a + b) * 3 from root.sg, root.lnNested Expressions query with aggregations
IoTDB > select avg(temperature),
sin(avg(temperature)),
avg(temperature) + 1,
-sum(hardware),
avg(temperature) + sum(hardware)
from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
IoTDB > select avg(*),
(avg(*) + 1) * 3 / 2 -1
from root.sg1
IoTDB > select avg(temperature),
sin(avg(temperature)),
avg(temperature) + 1,
-sum(hardware),
avg(temperature) + sum(hardware) as custom_sum
from root.ln.wf01.wt01
GROUP BY([10, 90), 10ms);Last Query
IoTDB > select last status from root.ln.wf01.wt01
IoTDB > select last status, temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time >= 2017-11-07T23:50:00
IoTDB > select last * from root.ln.wf01.wt01 order by timeseries desc;
IoTDB > select last * from root.ln.wf01.wt01 order by dataType desc;WHERE CLAUSE
Time Filter
IoTDB > select s1 from root.sg1.d1 where time > 2022-01-01T00:05:00.000;
IoTDB > select s1 from root.sg1.d1 where time = 2022-01-01T00:05:00.000;
IoTDB > select s1 from root.sg1.d1 where time >= 2022-01-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000;Value Filter
IoTDB > select temperature from root.sg1.d1 where temperature > 36.5;
IoTDB > select status from root.sg1.d1 where status = true;
IoTDB > select temperature from root.sg1.d1 where temperature between 36.5 and 40;
IoTDB > select temperature from root.sg1.d1 where temperature not between 36.5 and 40;
IoTDB > select code from root.sg1.d1 where code in ('200', '300', '400', '500');
IoTDB > select code from root.sg1.d1 where code not in ('200', '300', '400', '500');
IoTDB > select code from root.sg1.d1 where temperature is null;
IoTDB > select code from root.sg1.d1 where temperature is not null;Fuzzy Query
- Fuzzy matching using
Like
IoTDB > select * from root.sg.d1 where value like '%cc%'
IoTDB > select * from root.sg.device where value like '_b_'- Fuzzy matching using
Regexp
IoTDB > select * from root.sg.d1 where value regexp '^[A-Za-z]+$'
IoTDB > select * from root.sg.d1 where value regexp '^[a-z]+$' and time > 100GROUP BY CLAUSE
- Aggregate By Time without Specifying the Sliding Step Length
IoTDB > select count(status), max_value(temperature) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ([2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2017-11-07T23:00:00),1d);- Aggregate By Time Specifying the Sliding Step Length
IoTDB > select count(status), max_value(temperature) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ([2017-11-01 00:00:00, 2017-11-07 23:00:00), 3h, 1d);- Aggregate by Natural Month
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by([2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2019-11-07T23:00:00), 1mo, 2mo);
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by([2017-10-31T00:00:00, 2019-11-07T23:00:00), 1mo, 2mo);- Left Open And Right Close Range
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ((2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2017-11-07T23:00:00],1d);- Aggregation By Variation
IoTDB > select __endTime, avg(s1), count(s2), sum(s3) from root.sg.d group by variation(s6)
IoTDB > select __endTime, avg(s1), count(s2), sum(s3) from root.sg.d group by variation(s6, ignoreNull=false)
IoTDB > select __endTime, avg(s1), count(s2), sum(s3) from root.sg.d group by variation(s6, 4)
IoTDB > select __endTime, avg(s1), count(s2), sum(s3) from root.sg.d group by variation(s6+s5, 10)- Aggregation By Condition
IoTDB > select max_time(charging_status),count(vehicle_status),last_value(soc) from root.** group by condition(charging_status=1,KEEP>=2,ignoringNull=true)
IoTDB > select max_time(charging_status),count(vehicle_status),last_value(soc) from root.** group by condition(charging_status=1,KEEP>=2,ignoringNull=false)- Aggregation By Session
IoTDB > select __endTime,count(*) from root.** group by session(1d)
IoTDB > select __endTime,sum(hardware) from root.ln.wf02.wt01 group by session(50s) having sum(hardware)>0 align by device- Aggregation By Count
IoTDB > select count(charging_stauts), first_value(soc) from root.sg group by count(charging_status,5)
IoTDB > select count(charging_stauts), first_value(soc) from root.sg group by count(charging_status,5,ignoreNull=false)- Aggregation By Level
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.** group by level = 1
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.** group by level = 3
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.** group by level = 1, 3
IoTDB > select max_value(temperature) from root.** group by level = 0
IoTDB > select count(*) from root.ln.** group by level = 2- Aggregate By Time with Level Clause
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ((2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2017-11-07T23:00:00],1d), level=1;
IoTDB > select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ([2017-11-01 00:00:00, 2017-11-07 23:00:00), 3h, 1d), level=1;- Aggregation query by one single tag
IoTDB > SELECT AVG(temperature) FROM root.factory1.** GROUP BY TAGS(city);- Aggregation query by multiple tags
IoTDB > SELECT avg(temperature) FROM root.factory1.** GROUP BY TAGS(city, workshop);- Downsampling Aggregation by tags based on Time Window
IoTDB > SELECT avg(temperature) FROM root.factory1.** GROUP BY ([1000, 10000), 5s), TAGS(city, workshop);HAVING CLAUSE
Correct:
IoTDB > select count(s1) from root.** group by ([1,11),2ms), level=1 having count(s2) > 1
IoTDB > select count(s1), count(s2) from root.** group by ([1,11),2ms) having count(s2) > 1 align by deviceIncorrect:
IoTDB > select count(s1) from root.** group by ([1,3),1ms) having sum(s1) > s1
IoTDB > select count(s1) from root.** group by ([1,3),1ms) having s1 > 1
IoTDB > select count(s1) from root.** group by ([1,3),1ms), level=1 having sum(d1.s1) > 1
IoTDB > select count(d1.s1) from root.** group by ([1,3),1ms), level=1 having sum(s1) > 1FILL CLAUSE
PREVIOUS Fill
IoTDB > select temperature, status from root.sgcc.wf03.wt01 where time >= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:40:00.000 fill(previous);LINEAR Fill
IoTDB > select temperature, status from root.sgcc.wf03.wt01 where time >= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:40:00.000 fill(linear);Constant Fill
IoTDB > select temperature, status from root.sgcc.wf03.wt01 where time >= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:40:00.000 fill(2.0);
IoTDB > select temperature, status from root.sgcc.wf03.wt01 where time >= 2017-11-01T16:37:00.000 and time <= 2017-11-01T16:40:00.000 fill(true);LIMIT and SLIMIT CLAUSES (PAGINATION)
Row Control over Query Results
IoTDB > select status, temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 limit 10
IoTDB > select status, temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 limit 5 offset 3
IoTDB > select status,temperature from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time< 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000 limit 2 offset 3
IoTDB > select count(status), max_value(temperature) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ([2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2017-11-07T23:00:00),1d) limit 5 offset 3Column Control over Query Results
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000 slimit 1
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.wf01.wt01 where time > 2017-11-01T00:05:00.000 and time < 2017-11-01T00:12:00.000 slimit 1 soffset 1
IoTDB > select max_value(*) from root.ln.wf01.wt01 group by ([2017-11-01T00:00:00, 2017-11-07T23:00:00),1d) slimit 1 soffset 1Row and Column Control over Query Results
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.wf01.wt01 limit 10 offset 100 slimit 2 soffset 0ORDER BY CLAUSE
Order by in ALIGN BY TIME mode
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time <= 2017-11-01T00:01:00 order by time desc;Order by in ALIGN BY DEVICE mode
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time <= 2017-11-01T00:01:00 order by device desc,time asc align by device;
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time <= 2017-11-01T00:01:00 order by time asc,device desc align by device;
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time <= 2017-11-01T00:01:00 align by device;
IoTDB > select count(*) from root.ln.** group by ((2017-11-01T00:00:00.000+08:00,2017-11-01T00:03:00.000+08:00],1m) order by device asc,time asc align by deviceOrder by arbitrary expressions
IoTDB > select score from root.** order by score desc align by device
IoTDB > select score,total from root.one order by base+score+bonus desc
IoTDB > select score,total from root.one order by total desc
IoTDB > select base, score, bonus, total from root.** order by total desc NULLS Last,
score desc NULLS Last,
bonus desc NULLS Last,
time desc align by device
IoTDB > select min_value(total) from root.** order by min_value(total) asc align by device
IoTDB > select min_value(total),max_value(base) from root.** order by max_value(total) desc align by device
IoTDB > select score from root.** order by device asc, score desc, time asc align by deviceALIGN BY CLAUSE
Align by Device
IoTDB > select * from root.ln.** where time <= 2017-11-01T00:01:00 align by device;INTO CLAUSE (QUERY WRITE-BACK)
IoTDB > select s1, s2 into root.sg_copy.d1(t1), root.sg_copy.d2(t1, t2), root.sg_copy.d1(t2) from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2;
IoTDB > select count(s1 + s2), last_value(s2) into root.agg.count(s1_add_s2), root.agg.last_value(s2) from root.sg.d1 group by ([0, 100), 10ms);
IoTDB > select s1, s2 into root.sg_copy.d1(t1, t2), root.sg_copy.d2(t1, t2) from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2 align by device;
IoTDB > select s1 + s2 into root.expr.add(d1s1_d1s2), root.expr.add(d2s1_d2s2) from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2 align by device;- Using variable placeholders:
IoTDB > select s1, s2
into root.sg_copy.d1(::), root.sg_copy.d2(s1), root.sg_copy.d1(${3}), root.sg_copy.d2(::)
from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2;
IoTDB > select d1.s1, d1.s2, d2.s3, d3.s4
into ::(s1_1, s2_2), root.sg.d2_2(s3_3), root.${2}_copy.::(s4)
from root.sg;
IoTDB > select * into root.sg_bk.::(::) from root.sg.**;
IoTDB > select s1, s2, s3, s4
into root.backup_sg.d1(s1, s2, s3, s4), root.backup_sg.d2(::), root.sg.d3(backup_${4})
from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2, root.sg.d3
align by device;
IoTDB > select avg(s1), sum(s2) + sum(s3), count(s4)
into root.agg_${2}.::(avg_s1, sum_s2_add_s3, count_s4)
from root.**
align by device;
IoTDB > select * into ::(backup_${4}) from root.sg.** align by device;
IoTDB > select s1, s2 into root.sg_copy.d1(t1, t2), aligned root.sg_copy.d2(t1, t2) from root.sg.d1, root.sg.d2 align by device;OPERATOR
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
Arithmetic Operators
For details and examples, see the document Arithmetic Operators and Functions.
select s1, - s1, s2, + s2, s1 + s2, s1 - s2, s1 * s2, s1 / s2, s1 % s2 from root.sg.d1Comparison Operators
For details and examples, see the document Comparison Operators and Functions.
# Basic comparison operators
select a, b, a > 10, a <= b, !(a <= b), a > 10 && a > b from root.test;
# `BETWEEN ... AND ...` operator
select temperature from root.sg1.d1 where temperature between 36.5 and 40;
select temperature from root.sg1.d1 where temperature not between 36.5 and 40;
# Fuzzy matching operator: Use `Like` for fuzzy matching
select * from root.sg.d1 where value like '%cc%'
select * from root.sg.device where value like '_b_'
# Fuzzy matching operator: Use `Regexp` for fuzzy matching
select * from root.sg.d1 where value regexp '^[A-Za-z]+$'
select * from root.sg.d1 where value regexp '^[a-z]+$' and time > 100
select b, b like '1%', b regexp '[0-2]' from root.test;
# `IS NULL` operator
select code from root.sg1.d1 where temperature is null;
select code from root.sg1.d1 where temperature is not null;
# `IN` operator
select code from root.sg1.d1 where code in ('200', '300', '400', '500');
select code from root.sg1.d1 where code not in ('200', '300', '400', '500');
select a, a in (1, 2) from root.test;Logical Operators
For details and examples, see the document Logical Operators.
select a, b, a > 10, a <= b, !(a <= b), a > 10 && a > b from root.test;BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
Aggregate Functions
For details and examples, see the document Aggregate Functions.
select count(status) from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
select count_if(s1=0 & s2=0, 3), count_if(s1=1 & s2=0, 3) from root.db.d1;
select count_if(s1=0 & s2=0, 3, 'ignoreNull'='false'), count_if(s1=1 & s2=0, 3, 'ignoreNull'='false') from root.db.d1;
select time_duration(s1) from root.db.d1;Arithmetic Functions
For details and examples, see the document Arithmetic Operators and Functions.
select s1, sin(s1), cos(s1), tan(s1) from root.sg1.d1 limit 5 offset 1000;
select s4,round(s4),round(s4,2),round(s4,-1) from root.sg1.d1;Comparison Functions
For details and examples, see the document Comparison Operators and Functions.
select ts, on_off(ts, 'threshold'='2') from root.test;
select ts, in_range(ts, 'lower'='2', 'upper'='3.1') from root.test;String Processing Functions
For details and examples, see the document String Processing.
select s1, string_contains(s1, 's'='warn') from root.sg1.d4;
select s1, string_matches(s1, 'regex'='[^\\s]+37229') from root.sg1.d4;
select s1, length(s1) from root.sg1.d1
select s1, locate(s1, "target"="1") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, locate(s1, "target"="1", "reverse"="true") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, startswith(s1, "target"="1") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, endswith(s1, "target"="1") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, s2, concat(s1, s2, "target1"="IoT", "target2"="DB") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, s2, concat(s1, s2, "target1"="IoT", "target2"="DB", "series_behind"="true") from root.sg1.d1
select s1, substring(s1 from 1 for 2) from root.sg1.d1
select s1, replace(s1, 'es', 'tt') from root.sg1.d1
select s1, upper(s1) from root.sg1.d1
select s1, lower(s1) from root.sg1.d1
select s3, trim(s3) from root.sg1.d1
select s1, s2, strcmp(s1, s2) from root.sg1.d1
select strreplace(s1, "target"=",", "replace"="/", "limit"="2") from root.test.d1
select strreplace(s1, "target"=",", "replace"="/", "limit"="1", "offset"="1", "reverse"="true") from root.test.d1
select regexmatch(s1, "regex"="\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+", "group"="0") from root.test.d1
select regexreplace(s1, "regex"="192\.168\.0\.(\d+)", "replace"="cluster-$1", "limit"="1") from root.test.d1
select regexsplit(s1, "regex"=",", "index"="-1") from root.test.d1
select regexsplit(s1, "regex"=",", "index"="3") from root.test.d1Data Type Conversion Function
For details and examples, see the document Data Type Conversion Function.
SELECT cast(s1 as INT32) from root.sgConstant Timeseries Generating Functions
For details and examples, see the document Constant Timeseries Generating Functions.
select s1, s2, const(s1, 'value'='1024', 'type'='INT64'), pi(s2), e(s1, s2) from root.sg1.d1;Selector Functions
For details and examples, see the document Selector Functions.
select s1, top_k(s1, 'k'='2'), bottom_k(s1, 'k'='2') from root.sg1.d2 where time > 2020-12-10T20:36:15.530+08:00;Continuous Interval Functions
For details and examples, see the document Continuous Interval Functions.
select s1, zero_count(s1), non_zero_count(s2), zero_duration(s3), non_zero_duration(s4) from root.sg.d2;Variation Trend Calculation Functions
For details and examples, see the document Variation Trend Calculation Functions.
select s1, time_difference(s1), difference(s1), non_negative_difference(s1), derivative(s1), non_negative_derivative(s1) from root.sg1.d1 limit 5 offset 1000;
SELECT DIFF(s1), DIFF(s2) from root.test;
SELECT DIFF(s1, 'ignoreNull'='false'), DIFF(s2, 'ignoreNull'='false') from root.test;Sample Functions
For details and examples, see the document Sample Functions.
select equal_size_bucket_random_sample(temperature,'proportion'='0.1') as random_sample from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
select equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature, 'type'='avg','proportion'='0.1') as agg_avg, equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature, 'type'='max','proportion'='0.1') as agg_max, equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature,'type'='min','proportion'='0.1') as agg_min, equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature, 'type'='sum','proportion'='0.1') as agg_sum, equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature, 'type'='extreme','proportion'='0.1') as agg_extreme, equal_size_bucket_agg_sample(temperature, 'type'='variance','proportion'='0.1') as agg_variance from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
select equal_size_bucket_m4_sample(temperature, 'proportion'='0.1') as M4_sample from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
select equal_size_bucket_outlier_sample(temperature, 'proportion'='0.1', 'type'='avg', 'number'='2') as outlier_avg_sample, equal_size_bucket_outlier_sample(temperature, 'proportion'='0.1', 'type'='stendis', 'number'='2') as outlier_stendis_sample, equal_size_bucket_outlier_sample(temperature, 'proportion'='0.1', 'type'='cos', 'number'='2') as outlier_cos_sample, equal_size_bucket_outlier_sample(temperature, 'proportion'='0.1', 'type'='prenextdis', 'number'='2') as outlier_prenextdis_sample from root.ln.wf01.wt01;
select M4(s1,'timeInterval'='25','displayWindowBegin'='0','displayWindowEnd'='100') from root.vehicle.d1
select M4(s1,'windowSize'='10') from root.vehicle.d1Change Points Function
For details and examples, see the document Time-Series.
select change_points(s1), change_points(s2), change_points(s3), change_points(s4), change_points(s5), change_points(s6) from root.testChangePoints.d1DATA QUALITY FUNCTION LIBRARY
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
Data Quality
For details and examples, see the document Data-Quality.
# Completeness
select completeness(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
select completeness(s1,"window"="15") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:01:00
# Consistency
select consistency(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
select consistency(s1,"window"="15") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:01:00
# Timeliness
select timeliness(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
select timeliness(s1,"window"="15") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:01:00
# Validity
select Validity(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
select Validity(s1,"window"="15") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:01:00
# Accuracy
select Accuracy(t1,t2,t3,m1,m2,m3) from root.testData Profiling
For details and examples, see the document Data-Profiling.
# ACF
select acf(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:05
# Distinct
select distinct(s2) from root.test.d2
# Histogram
select histogram(s1,"min"="1","max"="20","count"="10") from root.test.d1
# Integral
select integral(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:10
select integral(s1, "unit"="1m") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:10
# IntegralAvg
select integralavg(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:10
# Mad
select mad(s0) from root.test
select mad(s0, "error"="0.01") from root.test
# Median
select median(s0, "error"="0.01") from root.test
# MinMax
select minmax(s1) from root.test
# Mode
select mode(s2) from root.test.d2
# MvAvg
select mvavg(s1, "window"="3") from root.test
# PACF
select pacf(s1, "lag"="5") from root.test
# Percentile
select percentile(s0, "rank"="0.2", "error"="0.01") from root.test
# Quantile
select quantile(s0, "rank"="0.2", "K"="800") from root.test
# Period
select period(s1) from root.test.d3
# QLB
select QLB(s1) from root.test.d1
# Resample
select resample(s1,'every'='5m','interp'='linear') from root.test.d1
select resample(s1,'every'='30m','aggr'='first') from root.test.d1
select resample(s1,'every'='30m','start'='2021-03-06 15:00:00') from root.test.d1
# Sample
select sample(s1,'method'='reservoir','k'='5') from root.test.d1
select sample(s1,'method'='isometric','k'='5') from root.test.d1
# Segment
select segment(s1, "error"="0.1") from root.test
# Skew
select skew(s1) from root.test.d1
# Spline
select spline(s1, "points"="151") from root.test
# Spread
select spread(s1) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
# Stddev
select stddev(s1) from root.test.d1
# ZScore
select zscore(s1) from root.testAnomaly Detection
For details and examples, see the document Anomaly-Detection.
# IQR
select iqr(s1) from root.test
# KSigma
select ksigma(s1,"k"="1.0") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
# LOF
select lof(s1,s2) from root.test.d1 where time<1000
select lof(s1, "method"="series") from root.test.d1 where time<1000
# MissDetect
select missdetect(s2,'minlen'='10') from root.test.d2
# Range
select range(s1,"lower_bound"="101.0","upper_bound"="125.0") from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:30
# TwoSidedFilter
select TwoSidedFilter(s0, 'len'='5', 'threshold'='0.3') from root.test
# Outlier
select outlier(s1,"r"="5.0","k"="4","w"="10","s"="5") from root.test
# MasterTrain
select MasterTrain(lo,la,m_lo,m_la,'p'='3','eta'='1.0') from root.test
# MasterDetect
select MasterDetect(lo,la,m_lo,m_la,model,'output_type'='repair','p'='3','k'='3','eta'='1.0') from root.test
select MasterDetect(lo,la,m_lo,m_la,model,'output_type'='anomaly','p'='3','k'='3','eta'='1.0') from root.testFrequency Domain
For details and examples, see the document Frequency-Domain.
# Conv
select conv(s1,s2) from root.test.d2
# Deconv
select deconv(s3,s2) from root.test.d2
select deconv(s3,s2,'result'='remainder') from root.test.d2
# DWT
select dwt(s1,"method"="haar") from root.test.d1
# FFT
select fft(s1) from root.test.d1
select fft(s1, 'result'='real', 'compress'='0.99'), fft(s1, 'result'='imag','compress'='0.99') from root.test.d1
# HighPass
select highpass(s1,'wpass'='0.45') from root.test.d1
# IFFT
select ifft(re, im, 'interval'='1m', 'start'='2021-01-01 00:00:00') from root.test.d1
# LowPass
select lowpass(s1,'wpass'='0.45') from root.test.d1Data Matching
For details and examples, see the document Data-Matching.
# Cov
select cov(s1,s2) from root.test.d2
# DTW
select dtw(s1,s2) from root.test.d2
# Pearson
select pearson(s1,s2) from root.test.d2
# PtnSym
select ptnsym(s4, 'window'='5', 'threshold'='0') from root.test.d1
# XCorr
select xcorr(s1, s2) from root.test.d1 where time <= 2020-01-01 00:00:05Data Repairing
For details and examples, see the document Data-Repairing.
# TimestampRepair
select timestamprepair(s1,'interval'='10000') from root.test.d2
select timestamprepair(s1) from root.test.d2
# ValueFill
select valuefill(s1) from root.test.d2
select valuefill(s1,"method"="previous") from root.test.d2
# ValueRepair
select valuerepair(s1) from root.test.d2
select valuerepair(s1,'method'='LsGreedy') from root.test.d2
# MasterRepair
select MasterRepair(t1,t2,t3,m1,m2,m3) from root.test
# SeasonalRepair
select seasonalrepair(s1,'period'=3,'k'=2) from root.test.d2
select seasonalrepair(s1,'method'='improved','period'=3) from root.test.d2Series Discovery
For details and examples, see the document Series-Discovery.
# ConsecutiveSequences
select consecutivesequences(s1,s2,'gap'='5m') from root.test.d1
select consecutivesequences(s1,s2) from root.test.d1
# ConsecutiveWindows
select consecutivewindows(s1,s2,'length'='10m') from root.test.d1Machine Learning
For details and examples, see the document Machine-Learning.
# AR
select ar(s0,"p"="2") from root.test.d0
# Representation
select representation(s0,"tb"="3","vb"="2") from root.test.d0
# RM
select rm(s0, s1,"tb"="3","vb"="2") from root.test.d0LAMBDA EXPRESSION
For details and examples, see the document Lambda.
select jexl(temperature, 'expr'='x -> {x + x}') as jexl1, jexl(temperature, 'expr'='x -> {x * 3}') as jexl2, jexl(temperature, 'expr'='x -> {x * x}') as jexl3, jexl(temperature, 'expr'='x -> {multiply(x, 100)}') as jexl4, jexl(temperature, st, 'expr'='(x, y) -> {x + y}') as jexl5, jexl(temperature, st, str, 'expr'='(x, y, z) -> {x + y + z}') as jexl6 from root.ln.wf01.wt01;```CONDITIONAL EXPRESSION
For details and examples, see the document Conditional Expressions.
select T, P, case
when 1000<T and T<1050 and 1000000<P and P<1100000 then "good!"
when T<=1000 or T>=1050 then "bad temperature"
when P<=1000000 or P>=1100000 then "bad pressure"
end as `result`
from root.test1
select str, case
when str like "%cc%" then "has cc"
when str like "%dd%" then "has dd"
else "no cc and dd" end as `result`
from root.test2
select
count(case when x<=1 then 1 end) as `(-∞,1]`,
count(case when 1<x and x<=3 then 1 end) as `(1,3]`,
count(case when 3<x and x<=7 then 1 end) as `(3,7]`,
count(case when 7<x then 1 end) as `(7,+∞)`
from root.test3
select x, case x when 1 then "one" when 2 then "two" else "other" end from root.test4
select x, case x when 1 then true when 2 then false end as `result` from root.test4
select x, case x
when 1 then 1
when 2 then 222222222222222
when 3 then 3.3
when 4 then 4.4444444444444
end as `result`
from root.test4TRIGGER
For more details, see document Database-Programming.
Create Trigger
// Create Trigger
createTrigger
: CREATE triggerType TRIGGER triggerName=identifier triggerEventClause ON pathPattern AS className=STRING_LITERAL uriClause? triggerAttributeClause?
;
triggerType
: STATELESS | STATEFUL
;
triggerEventClause
: (BEFORE | AFTER) INSERT
;
uriClause
: USING URI uri
;
uri
: STRING_LITERAL
;
triggerAttributeClause
: WITH LR_BRACKET triggerAttribute (COMMA triggerAttribute)* RR_BRACKET
;
triggerAttribute
: key=attributeKey operator_eq value=attributeValue
;Drop Trigger
// Drop Trigger
dropTrigger
: DROP TRIGGER triggerName=identifier
;Show Trigger
SHOW TRIGGERSCONTINUOUS QUERY (CQ)
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
CREATE (CONTINUOUS QUERY | CQ) <cq_id>
[RESAMPLE
[EVERY <every_interval>]
[BOUNDARY <execution_boundary_time>]
[RANGE <start_time_offset>[, end_time_offset]]
]
[TIMEOUT POLICY BLOCKED|DISCARD]
BEGIN
SELECT CLAUSE
INTO CLAUSE
FROM CLAUSE
[WHERE CLAUSE]
[GROUP BY(<group_by_interval>[, <sliding_step>]) [, level = <level>]]
[HAVING CLAUSE]
[FILL {PREVIOUS | LINEAR | constant}]
[LIMIT rowLimit OFFSET rowOffset]
[ALIGN BY DEVICE]
ENDConfiguring execution intervals
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq1
RESAMPLE EVERY 20s
BEGIN
SELECT max_value(temperature)
INTO root.ln.wf02.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf02.wt01(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt01(temperature_max)
FROM root.ln.*.*
GROUP BY(10s)
ENDConfiguring time range for resampling
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq2
RESAMPLE RANGE 40s
BEGIN
SELECT max_value(temperature)
INTO root.ln.wf02.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf02.wt01(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt01(temperature_max)
FROM root.ln.*.*
GROUP BY(10s)
ENDConfiguring execution intervals and CQ time ranges
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq3
RESAMPLE EVERY 20s RANGE 40s
BEGIN
SELECT max_value(temperature)
INTO root.ln.wf02.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf02.wt01(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt01(temperature_max)
FROM root.ln.*.*
GROUP BY(10s)
FILL(100.0)
ENDConfiguring end_time_offset for CQ time range
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq4
RESAMPLE EVERY 20s RANGE 40s, 20s
BEGIN
SELECT max_value(temperature)
INTO root.ln.wf02.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf02.wt01(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt02(temperature_max), root.ln.wf01.wt01(temperature_max)
FROM root.ln.*.*
GROUP BY(10s)
FILL(100.0)
ENDCQ without group by clause
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq5
RESAMPLE EVERY 20s
BEGIN
SELECT temperature + 1
INTO root.precalculated_sg.::(temperature)
FROM root.ln.*.*
align by device
ENDCQ Management
Listing continuous queries
SHOW (CONTINUOUS QUERIES | CQS)Dropping continuous queries
DROP (CONTINUOUS QUERY | CQ) <cq_id>Altering continuous queries
CQs can't be altered once they're created. To change a CQ, you must DROP and reCREATE it with the updated settings.
USER-DEFINED FUNCTION (UDF)
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
UDF Registration
CREATE FUNCTION <UDF-NAME> AS <UDF-CLASS-FULL-PATHNAME> (USING URI URI-STRING)?UDF Deregistration
DROP FUNCTION <UDF-NAME>UDF Queries
SELECT example(*) from root.sg.d1
SELECT example(s1, *) from root.sg.d1
SELECT example(*, *) from root.sg.d1
SELECT example(s1, 'key1'='value1', 'key2'='value2'), example(*, 'key3'='value3') FROM root.sg.d1;
SELECT example(s1, s2, 'key1'='value1', 'key2'='value2') FROM root.sg.d1;
SELECT s1, s2, example(s1, s2) FROM root.sg.d1;
SELECT *, example(*) FROM root.sg.d1 DISABLE ALIGN;
SELECT s1 * example(* / s1 + s2) FROM root.sg.d1;
SELECT s1, s2, s1 + example(s1, s2), s1 - example(s1 + example(s1, s2) / s2) FROM root.sg.d1;Show All Registered UDFs
SHOW FUNCTIONSADMINISTRATION MANAGEMENT
For more details, see document Operator-and-Expression.
SQL Statements
- Create User
CREATE USER <userName> <password>;
Eg: IoTDB > CREATE USER `thulab` 'pwd';- Delete User
DROP USER <userName>;
Eg: IoTDB > DROP USER `xiaoming`;- Create Role
CREATE ROLE <roleName>;
Eg: IoTDB > CREATE ROLE `admin`;- Delete Role
DROP ROLE <roleName>;
Eg: IoTDB > DROP ROLE `admin`;- Grant User Privileges
GRANT USER <userName> PRIVILEGES <privileges> ON <nodeNames>;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES INSERT_TIMESERIES, DELETE_TIMESERIES on root.ln.**, root.sgcc.**;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES CREATE_ROLE;- Grant User All Privileges
GRANT USER <userName> PRIVILEGES ALL;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES ALL;- Grant Role Privileges
GRANT ROLE <roleName> PRIVILEGES <privileges> ON <nodeNames>;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES INSERT_TIMESERIES, DELETE_TIMESERIES ON root.sgcc.**, root.ln.**;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES CREATE_ROLE;- Grant Role All Privileges
GRANT ROLE <roleName> PRIVILEGES ALL ON <nodeNames>;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES ALL;- Grant User Role
GRANT <roleName> TO <userName>;
Eg: IoTDB > GRANT `temprole` TO tempuser;- Revoke User Privileges
REVOKE USER <userName> PRIVILEGES <privileges> ON <nodeNames>;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES DELETE_TIMESERIES on root.ln.**;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES CREATE_ROLE;- Revoke User All Privileges
REVOKE USER <userName> PRIVILEGES ALL;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE USER `tempuser` PRIVILEGES ALL;- Revoke Role Privileges
REVOKE ROLE <roleName> PRIVILEGES <privileges> ON <nodeNames>;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES DELETE_TIMESERIES ON root.ln.**;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES CREATE_ROLE;- Revoke All Role Privileges
REVOKE ROLE <roleName> PRIVILEGES ALL;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE ROLE `temprole` PRIVILEGES ALL;- Revoke Role From User
REVOKE <roleName> FROM <userName>;
Eg: IoTDB > REVOKE `temprole` FROM tempuser;- List Users
LIST USER
Eg: IoTDB > LIST USER- List User of Specific Role
LIST USER OF ROLE <roleName>;
Eg: IoTDB > LIST USER OF ROLE `roleuser`;- List Roles
LIST ROLE
Eg: IoTDB > LIST ROLE- List Roles of Specific User
LIST ROLE OF USER <username> ;
Eg: IoTDB > LIST ROLE OF USER `tempuser`;- List All Privileges of Users
LIST PRIVILEGES USER <username> ;
Eg: IoTDB > LIST PRIVILEGES USER `tempuser`;- List Related Privileges of Users(On Specific Paths)
LIST PRIVILEGES USER <username> ON <paths>;
Eg: IoTDB> LIST PRIVILEGES USER `tempuser` ON root.ln.**, root.ln.wf01.**;
+--------+-----------------------------------+
| role| privilege|
+--------+-----------------------------------+
| | root.ln.** : ALTER_TIMESERIES|
|temprole|root.ln.wf01.** : CREATE_TIMESERIES|
+--------+-----------------------------------+
Total line number = 2
It costs 0.005s
IoTDB> LIST PRIVILEGES USER `tempuser` ON root.ln.wf01.wt01.**;
+--------+-----------------------------------+
| role| privilege|
+--------+-----------------------------------+
| | root.ln.** : ALTER_TIMESERIES|
|temprole|root.ln.wf01.** : CREATE_TIMESERIES|
+--------+-----------------------------------+
Total line number = 2
It costs 0.005s- List All Privileges of Roles
LIST PRIVILEGES ROLE <roleName>
Eg: IoTDB > LIST PRIVILEGES ROLE `actor`;- List Related Privileges of Roles(On Specific Paths)
LIST PRIVILEGES ROLE <roleName> ON <paths>;
Eg: IoTDB> LIST PRIVILEGES ROLE `temprole` ON root.ln.**, root.ln.wf01.wt01.**;
+-----------------------------------+
| privilege|
+-----------------------------------+
|root.ln.wf01.** : CREATE_TIMESERIES|
+-----------------------------------+
Total line number = 1
It costs 0.005s
IoTDB> LIST PRIVILEGES ROLE `temprole` ON root.ln.wf01.wt01.**;
+-----------------------------------+
| privilege|
+-----------------------------------+
|root.ln.wf01.** : CREATE_TIMESERIES|
+-----------------------------------+
Total line number = 1
It costs 0.005s- Alter Password
ALTER USER <username> SET PASSWORD <password>;
Eg: IoTDB > ALTER USER `tempuser` SET PASSWORD 'newpwd';Operations restricted by non root users
At present, the following SQL statements supported by iotdb can only be operated by the root user, and no corresponding permission can be given to the new user.
TsFile Management
- Load TsFiles
Eg: IoTDB > load '/Users/Desktop/data/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile'- remove a tsfile
Eg: IoTDB > remove '/Users/Desktop/data/data/root.vehicle/0/0/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile'- unload a tsfile and move it to a target directory
Eg: IoTDB > unload '/Users/Desktop/data/data/root.vehicle/0/0/1575028885956-101-0.tsfile' '/data/data/tmp'Delete Time Partition (experimental)
Eg: IoTDB > DELETE PARTITION root.ln 0,1,2Continuous Query,CQ
Eg: IoTDB > CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq1 BEGIN SELECT max_value(temperature) INTO temperature_max FROM root.ln.*.* GROUP BY time(10s) ENDMaintenance Command
- FLUSH
Eg: IoTDB > flush- MERGE
Eg: IoTDB > MERGE
Eg: IoTDB > FULL MERGE- CLEAR CACHE
Eg: IoTDB > CLEAR CACHE- SET SYSTEM TO READONLY / WRITABLE
Eg: IoTDB > SET SYSTEM TO READONLY / WRITABLE- Query abort
Eg: IoTDB > KILL QUERY 1Watermark Tool
- Watermark new users
Eg: IoTDB > grant watermark_embedding to Alice- Watermark Detection
Eg: IoTDB > revoke watermark_embedding from Alice